OUR SERVICES
IT Business Analysis
GMH Solutions provide IT Business Analysis services to support organizations of all sizes, spanning many different industries. Using effective communication, our Business Analysts work as liaisons between a variety of audiences, including business users, IT professionals and other stakeholders, in order to gather, analyze, communicate and validate requirements for changes to business processes, policies and information systems.
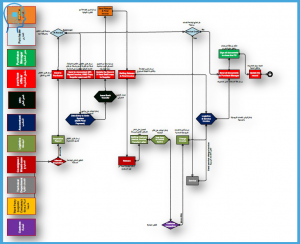
We work as a bridge between different stakeholders in an organization to clarify and finalize the requirements, then help the project team designing and finally validating the developed components. We possess adequate domain knowledge and can sort the business needs among the stakeholders who belong to different domains.
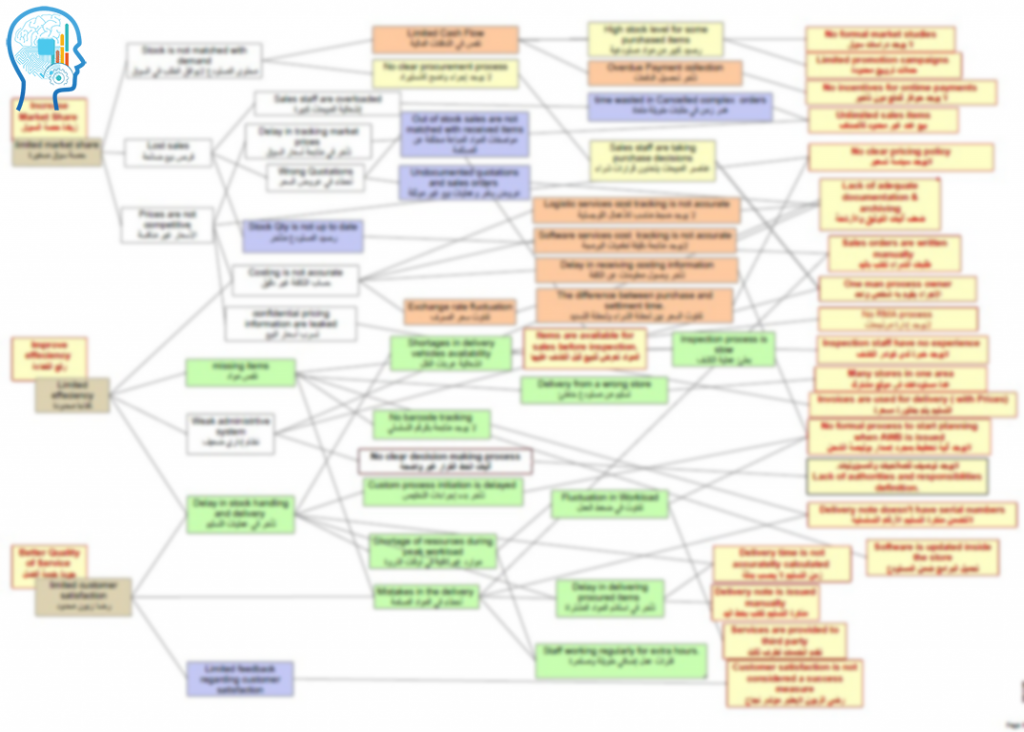
We handle at least the following documents:
- Project vision document
- Use cases
- Requirement Management Plan
- User stories
- Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM)
- Business Requirement Document
- System Requirement Specification (SRS)/ System Requirement Document (SRD)
- Test case
- Functional Requirement Specification (FRS)/ Functional Specification Document (FSD)
The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Gather Background Information – This may include collecting background information about the project, analyzing any potential risk associated with the project.
Step 2: Identify Stakeholders – They are the decision makers of a project and approver for requirements and priorities. Stakeholders may range from project owners to senior managers, end users, and even competitors.
Step 3: Discover Business Objectives – This is to understand the business needs of the project before going deep into the project. SWOT analysis, Benchmarking, analyzing business objectives SMART and listing business objectives are some of the techniques used for this purpose.
Step 4: Evaluate Options – This is to identify the options to achieve business objectives. Impact analysis, Risk analysis, Cost-benefit analysis are some of the methods which are used for this purpose.
Step 5: Scope Definition – A scope is a project development goal which is set based on the business objectives. A scope definition document is used to detail the goals for each phase of a project.
Step 6: Business Analyst Delivery Plan – Based on the project scope, stakeholders availability and project methodology a document called business analyst is created at this step. The document provides information on deliverables with their timeline.
Step 7: Define Project Requirements – In this step, two types of documents are used – Functional requirement document and Non-functional requirement document. Based on the development methodology to be used in the project the business analyst needs to clarify the requirements with the stakeholders by interviewing them on the requirements and get the sign off on the same.
Step 8: Support Implementation through SDLC – This is the technical implementation step of the requirements where a business analyst gets involved with different teams. This includes coordinating with the development team and testing team to ensure requirements are implemented as expected and appropriately tested against all the possible business scenarios. They also need to handle the change request which may arise from the stakeholders at the later point of time.
Step 9: Evaluate Value Added By Project – This is the continuous evaluation of the project to evaluate whether the business objectives implementation correctly meets the business needs outcome and timeline.
Business analysis is the practice of enabling change in an enterprise by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders
Benchmark
- Company One
- Company Two
- Company Three
System Requirement
A System Requirements Specification (SRS) or a Software Requirements Specification is a document or set of documents that describe the features of a system or software application. It includes a variety of elements which define the intended functionality required by the stakeholders and customer to satisfy the end users.
In addition to that, an SRS provides a high-level idea of the system and its behavior, the main supported business processes, the assumptions and the key performance parameters for the system. The key elements of an SRS are:
The Result You Can Expect
GMH Solutions provides a results-driven delivery process of IT solutions that are technology-agnostic and methodology-unbiased. Our analysts, solution architects, developers, and project managers are well trained and experienced in both contemporary and legacy software development technologies, traditional SDLC, and Agile development cycles.
Our Consultants bring extensive experience from multiple industries and disciplines to your team. Whether you’re engaging an entire team or simply augmenting a few key roles, you can be assured that our consultants will complement and strengthen your existing teams while providing the flexibility you need.
We can blend in and collaborate with your internal teams, or we can take full responsibility for a turn-key solution. Regardless of the format of work, we will deliver high-quality solutions that will meet or exceed your expectations.
By engaging GMH Solutions’s development and integration capabilities, you will shorten delivery cycles, meet your deadlines, keep your budget intact, and achieve your business goal.